Your Colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes images are available. Colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes images information related to the colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes interest, you have come to the right blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
Colonic Mucosa With Hyperplastic Changes. In 1992It is a nonneoplastic colorectal polyp with three main histological features. Inflammatory myoglandular polyp was first described by Nakamura et al. Most common in left colon especially the rectum. 1 hyperplastic glands with cystic dilatation 2 inflammatory granulation tissue in the lamina propria 3 proliferation of smooth muscle from the muscularis mucosa.
 Serrated Lesions Of The Colorectum Review And Recommendations From An Expert Panel Abstract Europe Pmc From europepmc.org
Serrated Lesions Of The Colorectum Review And Recommendations From An Expert Panel Abstract Europe Pmc From europepmc.org
An organ-culture system has been used to investigate the effect of certain gastrointestinal peptides on the morphology and cell proliferation of explants of azoxymethane AOM-treated colonic mucosa. Focal hyperplastic changes means that in a localised focal area there was an increase in the cells seen. However recent studies showed genetic mutations in tumor suppressor gene such as apc can be detected in majority of sporadic colon cancer while dna repair gene mutation account for some high risk colon cancer syndromes known as lynch syndrome. Inflammation in conjunction with the increased proliferation seen in hyperplastic polyps appears to be the stimulus for multinucleated epithelial giant cell MEG formation and the pro-inflammatory properties of sodium phosphate bowel preparation may be a factor in their. Because the ulcerated surface is thinner than normal the remaining normal mucosal patches protrude and resemble polyps. 1 hyperplastic glands with cystic dilatation 2 inflammatory granulation tissue in the lamina propria 3 proliferation of smooth muscle from the muscularis mucosa.
Some of the pseudopolyps represent hyperplastic granulation tissue intermixed with regenerating colonic epithelium.
The surface of intestinal mucosa stained with methylene-blue was studied in order to determine the number and localization of focal changes in the macroscopically unchanged areas. In 1992It is a nonneoplastic colorectal polyp with three main histological features. Even dilute solutions of. When an injury occurs the body works to repair the area. Becomes hyperplastic and hyperkeratotic. Hyperplastic changes in the mucosa in colon cancer 67 segments of rectum and sigmoid removed surgically because of carcinoma were examined.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They are a normal finding. Because the ulcerated surface is thinner than normal the remaining normal mucosal patches protrude and resemble polyps. Biopsy shows benign colonic mucosa with preserved crypt architecture however mild focal crept regenerative changes noted. Patient exposure usually occurs when the chemicals are inadvertently flushed onto colonic mucosa mixed with the lens-wash water from a colonoscope that was inadequately rinsed and dried after chemical sterilization between procedures. They are the most common colonic polyp 75 - 90 of colon polyps typically 1 - 5 mm in greatest dimension rarely 1 cm or greater.
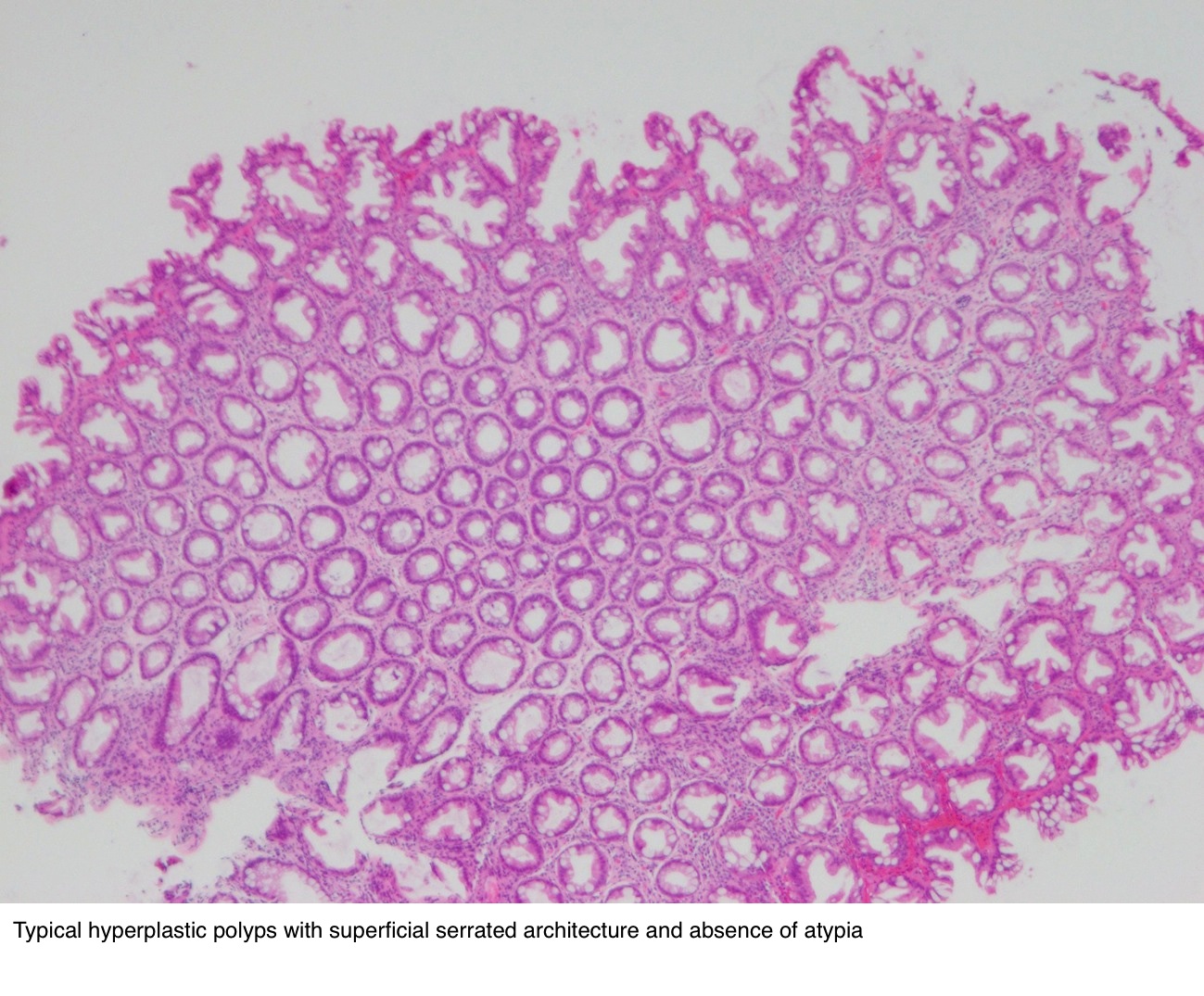 Source: pathologyoutlines.com
Source: pathologyoutlines.com
Becomes hyperplastic and hyperkeratotic. A quick check on the internet showed that hyperplastic polyps do not turn into colon cancer. Fragments of benign colonic mucosa with reactivehyper plastic changes and focal lymphoid aggregates. During this repair process polyps may form due to extra cell proliferation or abnormal repair. Because the ulcerated surface is thinner than normal the remaining normal mucosal patches protrude and resemble polyps.
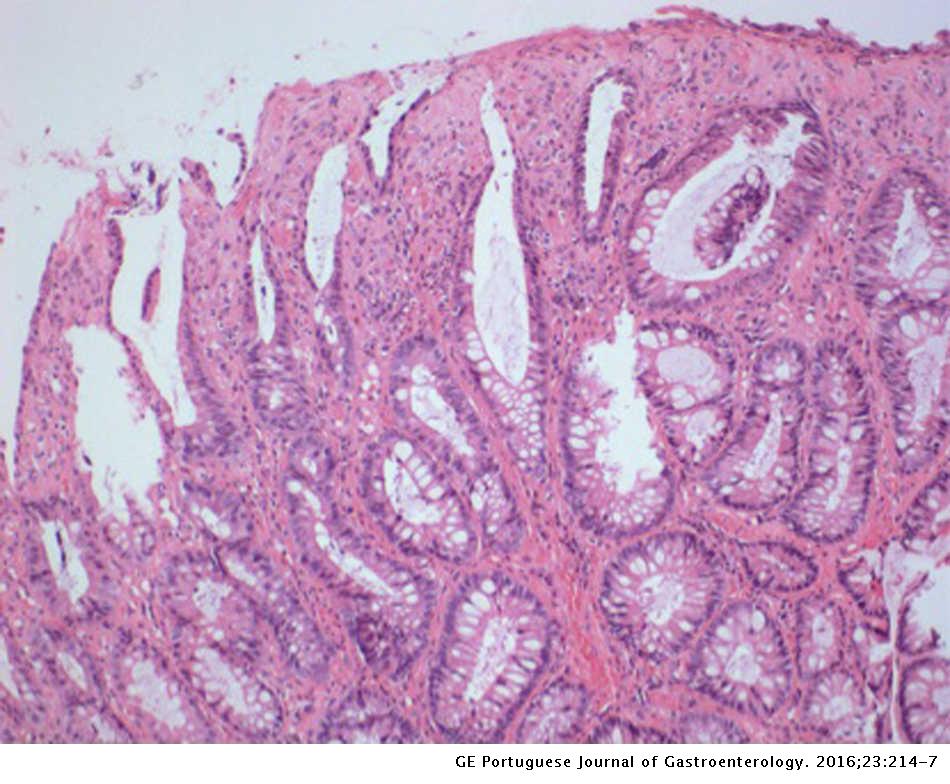 Source: elsevier.es
Source: elsevier.es
Biopsy shows benign colonic mucosa with preserved crypt architecture however mild focal crept regenerative changes noted. Failure to demonstrate specificity of morphological and histochemical changes in mucosa adjacent to colonic carcinoma transitional mucosa. A quick check on the internet showed that hyperplastic polyps do not turn into colon cancer. However recent studies showed genetic mutations in tumor suppressor gene such as apc can be detected in majority of sporadic colon cancer while dna repair gene mutation account for some high risk colon cancer syndromes known as lynch syndrome. Lymphoid aggregates are commonly found in the colon and small bowel.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Affected stomachs are heavier and may have a larger surface area than control stomachs. Most common in left colon especially the rectum. Patient exposure usually occurs when the chemicals are inadvertently flushed onto colonic mucosa mixed with the lens-wash water from a colonoscope that was inadequately rinsed and dried after chemical sterilization between procedures. Hyperplastic polyps HPs are asymptomatic and have no malignant potential. They are a normal finding.
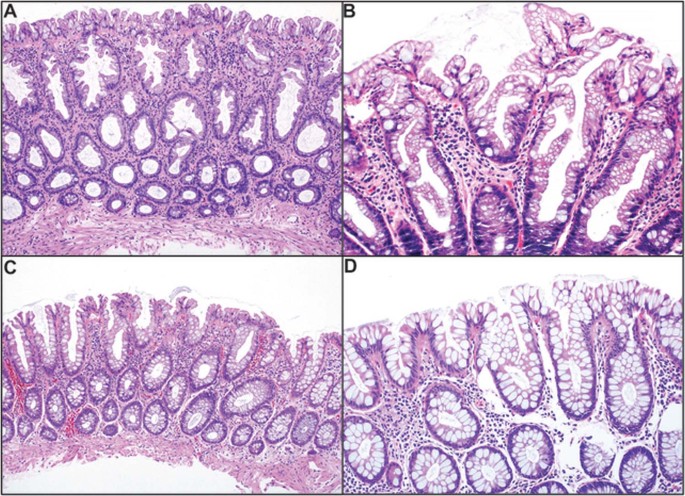 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
They are the most common colonic polyp 75 - 90 of colon polyps typically 1 - 5 mm in greatest dimension rarely 1 cm or greater. Unlike tubular and villous adenomas they do not predispose the patient to colonic cancer. Some of the pseudopolyps represent hyperplastic granulation tissue intermixed with regenerating colonic epithelium. They are a normal finding. These type of polyps are not thought to have any potential to become malignant unless they.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Multinucleate epithelial change in colorectal hyperplastic polyps is uncommon and may be mistaken for viral infection or dysplasia. In 1992It is a nonneoplastic colorectal polyp with three main histological features. 1 hyperplastic glands with cystic dilatation 2 inflammatory granulation tissue in the lamina propria 3 proliferation of smooth muscle from the muscularis mucosa. Adenomatous and carcinomatous changes within hyperplastic colonic epithelium. Hyperplastic colorectal polyps happen in your colon the lining of your large intestine.
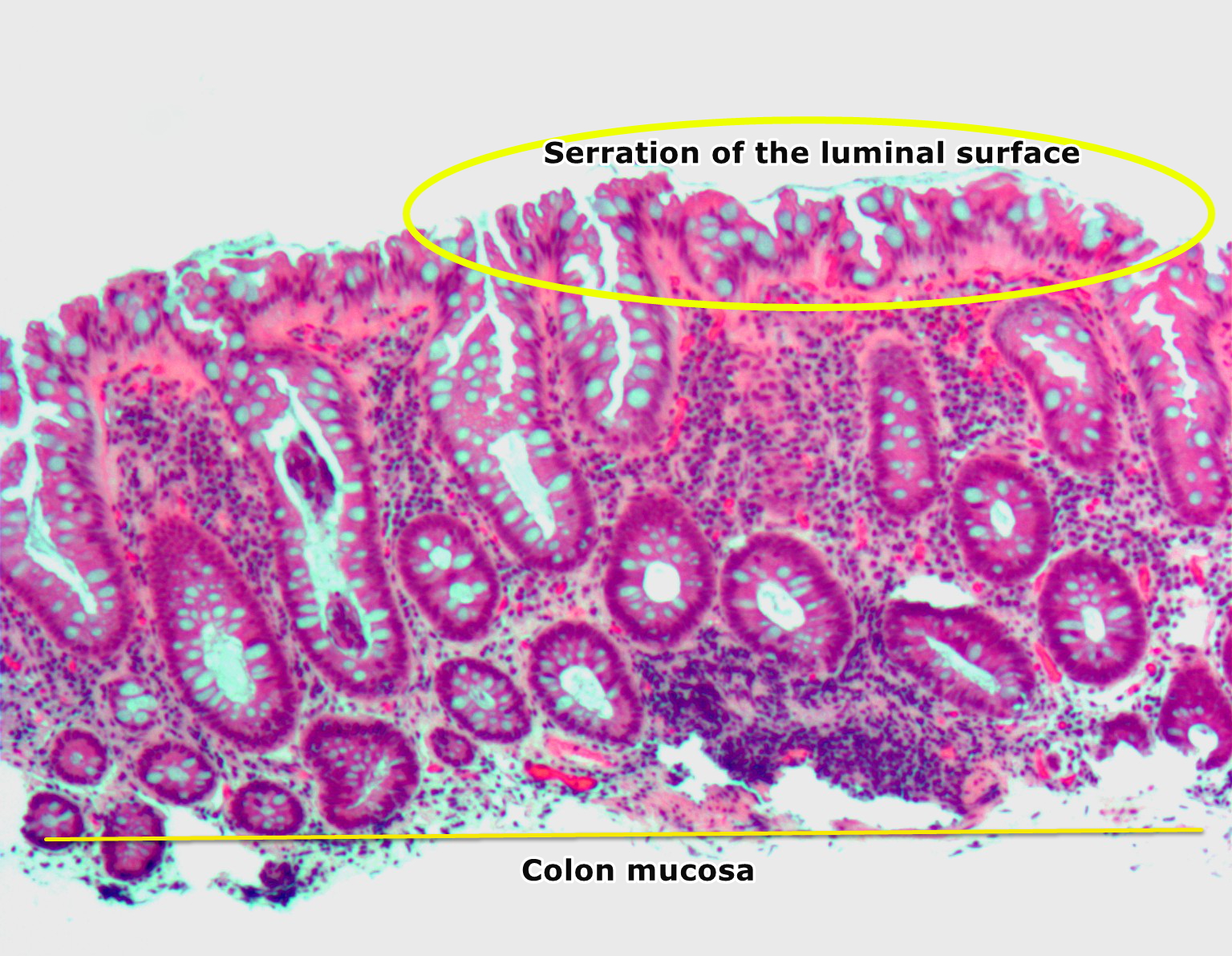 Source: wikidoc.org
Source: wikidoc.org
During this repair process polyps may form due to extra cell proliferation or abnormal repair. They are a normal finding. Lymphoid aggregates are commonly found in the colon and small bowel. Mild hyperplastic changes means a slight increase in cells of the mucosa and it can be due to infection or inflammation and usually it is a benign change so nothing much to worry aboutI would recommend you to followup with your doctor with the report for exact diagnosis depending on clinical correlations. However recent studies showed genetic mutations in tumor suppressor gene such as apc can be detected in majority of sporadic colon cancer while dna repair gene mutation account for some high risk colon cancer syndromes known as lynch syndrome.
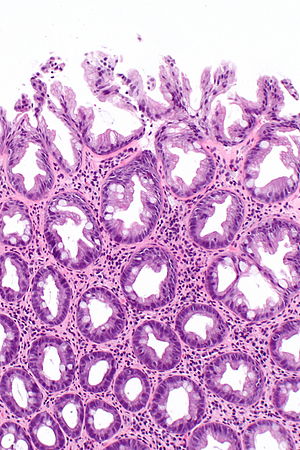 Source: librepathology.org
Source: librepathology.org
Fragments of benign colonic mucosa with reactivehyper plastic changes and focal lymphoid aggregates. Hyperplastic Polyps of the Colon are typically formed in response to colon injury or irritation. Pseudopolyps are remnants of normal or regenerating colonic mucosa surrounded by ulcerations. The cells pile up and form a polyp. Sialomucins were often predominant in the mucosa adjacent to large adenomas but N type mucosa was also seen near minute adenomas and hyperplastic polyps and remote from polypoid lesions.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Hyperplastic polyps HPs are asymptomatic and have no malignant potential. Our aim was to ascertain whether such factors play a direct part in the maintenance of hyperplastic changes in the large intestine. Mild hyperplastic changes means a slight increase in cells of the mucosa and it can be due to infection or inflammation and usually it is a benign change so nothing much to worry aboutI would recommend you to followup with your doctor with the report for exact diagnosis depending on clinical correlations. Inflammatory myoglandular polyp was first described by Nakamura et al. Hyperplastic Polyps of the Colon are typically formed in response to colon injury or irritation.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They are the most common colonic polyp 75 - 90 of colon polyps typically 1 - 5 mm in greatest dimension rarely 1 cm or greater. Hyperplastic colorectal polyps happen in your colon the lining of your large intestine. Hyperplastic Polyps of the Colon are typically formed in response to colon injury or irritation. They are a normal finding. In 1992It is a nonneoplastic colorectal polyp with three main histological features.
 Source: bigjuicycolon.com
Source: bigjuicycolon.com
Hyperplastic gastric or stomach polyps appear in the epithelium the layer of tissue that lines the inside. Mild hyperplastic changes means a slight increase in cells of the mucosa and it can be due to infection or inflammation and usually it is a benign change so nothing much to worry aboutI would recommend you to followup with your doctor with the report for exact diagnosis depending on clinical correlations. Moreover both hyperplastic and secretory changes were more frequent in the left colon than in the right. These type of polyps are not thought to have any potential to become malignant unless they. Adenomatous and carcinomatous changes within hyperplastic colonic epithelium.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Sialomucins were often predominant in the mucosa adjacent to large adenomas but N type mucosa was also seen near minute adenomas and hyperplastic polyps and remote from polypoid lesions. Hyperplastic Polyps of the Colon are typically formed in response to colon injury or irritation. They are a normal finding. Some of the pseudopolyps represent hyperplastic granulation tissue intermixed with regenerating colonic epithelium. Mild hyperplastic changes means a slight increase in cells of the mucosa and it can be due to infection or inflammation and usually it is a benign change so nothing much to worry aboutI would recommend you to followup with your doctor with the report for exact diagnosis depending on clinical correlations.
Source:
Colonic mucosa may exhibit mild hyperplasia at. The surface of intestinal mucosa stained with methylene-blue was studied in order to determine the number and localization of focal changes in the macroscopically unchanged areas. Small intestines may be heavier and have a thicker mucosa with elongation of villi and crypts. A quick check on the internet showed that hyperplastic polyps do not turn into colon cancer. These type of polyps are not thought to have any potential to become malignant unless they.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
During this repair process polyps may form due to extra cell proliferation or abnormal repair. Patient exposure usually occurs when the chemicals are inadvertently flushed onto colonic mucosa mixed with the lens-wash water from a colonoscope that was inadequately rinsed and dried after chemical sterilization between procedures. Hyperplastic changes in the mucosa in colon cancer 67 segments of rectum and sigmoid removed surgically because of carcinoma were examined. Biopsy shows benign colonic mucosa with preserved crypt architecture however mild focal crept regenerative changes noted. Lymphoid aggregates are commonly found in the colon and small bowel.
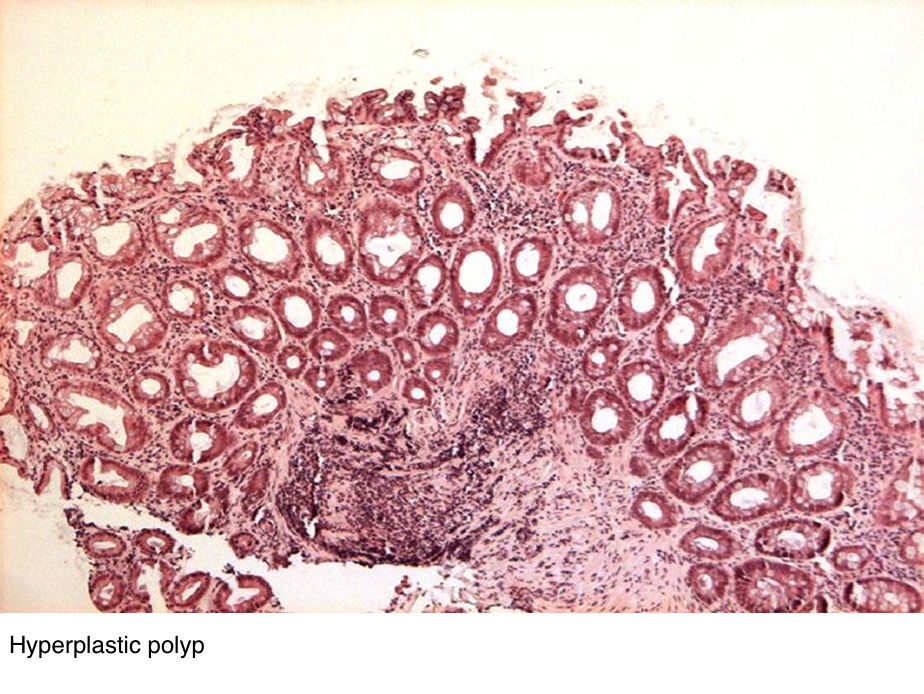 Source: pathologyoutlines.com
Source: pathologyoutlines.com
Inflammation in conjunction with the increased proliferation seen in hyperplastic polyps appears to be the stimulus for multinucleated epithelial giant cell MEG formation and the pro-inflammatory properties of sodium phosphate bowel preparation may be a factor in their. Moreover both hyperplastic and secretory changes were more frequent in the left colon than in the right. Pseudopolyps are remnants of normal or regenerating colonic mucosa surrounded by ulcerations. However as always with the net do not self-diagnosisrely on what your doctor has to offer. Our aim was to ascertain whether such factors play a direct part in the maintenance of hyperplastic changes in the large intestine.
 Source: wikidoc.org
Source: wikidoc.org
Small intestines may be heavier and have a thicker mucosa with elongation of villi and crypts. Hyperplastic changes in the mucosa in colon cancer 67 segments of rectum and sigmoid removed surgically because of carcinoma were examined. When an injury occurs the body works to repair the area. Focal hyperplastic changes means that in a localised focal area there was an increase in the cells seen. A quick check on the internet showed that hyperplastic polyps do not turn into colon cancer.
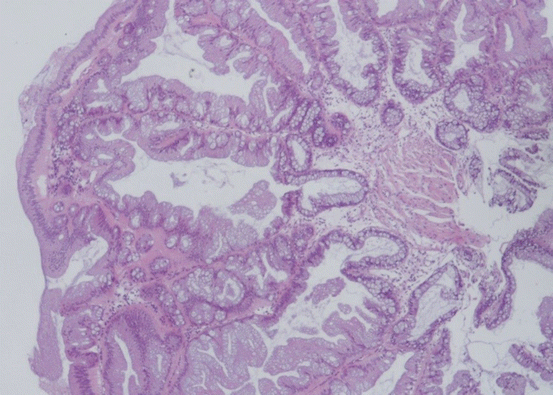 Source: oncohemakey.com
Source: oncohemakey.com
Small intestines may be heavier and have a thicker mucosa with elongation of villi and crypts. Hyperplastic colorectal polyps happen in your colon the lining of your large intestine. Failure to demonstrate specificity of morphological and histochemical changes in mucosa adjacent to colonic carcinoma transitional mucosa. Theoretically these hyperplastic polyps like normal colonic epithelium should be able to undergo adenomatous. Adenomatous and carcinomatous changes within hyperplastic colonic epithelium.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Lymphoid aggregates are commonly found in the colon and small bowel. These type of polyps are not thought to have any potential to become malignant unless they. The surface of intestinal mucosa stained with methylene-blue was studied in order to determine the number and localization of focal changes in the macroscopically unchanged areas. They are a normal finding. They are the most common colonic polyp 75 - 90 of colon polyps typically 1 - 5 mm in greatest dimension rarely 1 cm or greater.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title colonic mucosa with hyperplastic changes by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






